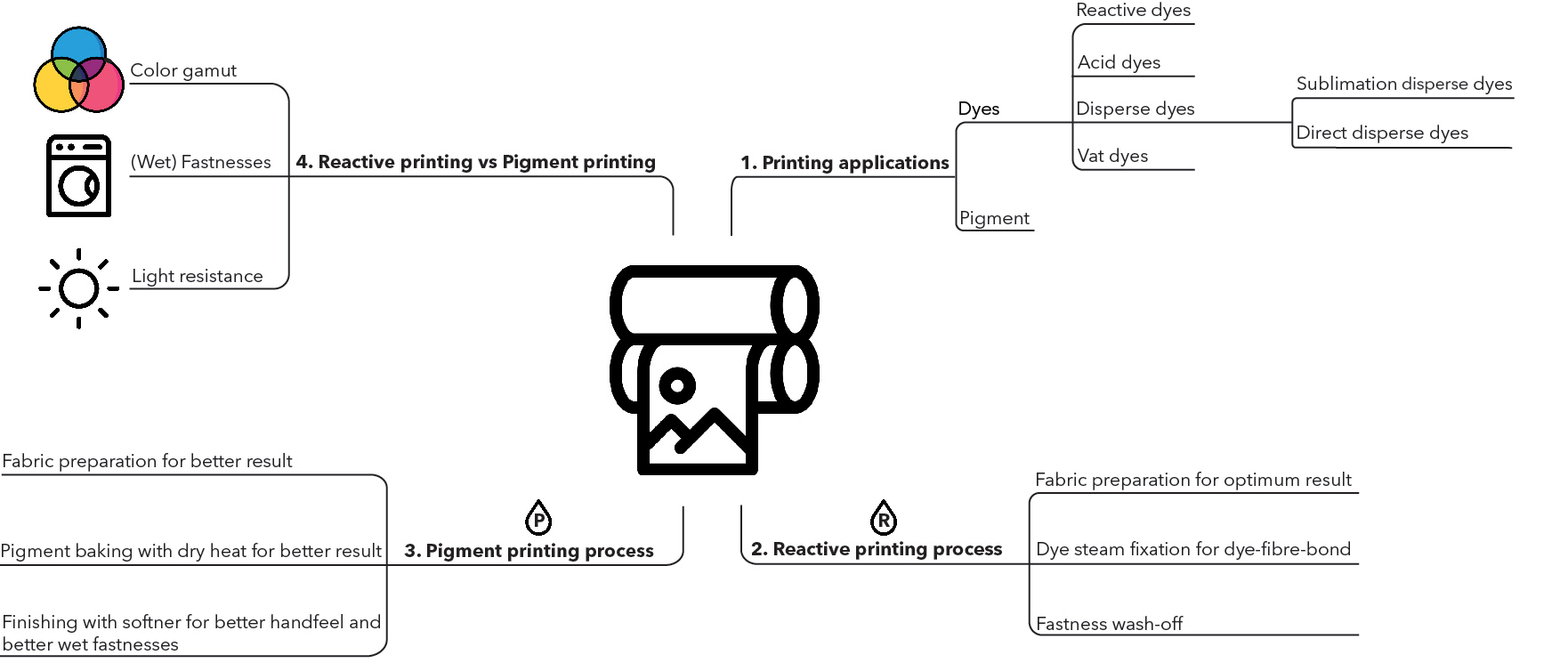
The printing applications
The 5 digital printing methods includes pigment ink printing, reactive dye printing, acid dye printing, disperse dye (direct disperse as well as sublimation disperse) printing and vat dye printing.
- Reactive dye on cotton, other plant derived fibres, viscose, and silk, for apparel and high-end fashion products, interior products, and accessories.
Characteristics: bright colors and good wash fastness due to chemical bond created between the dye and the fabric; relatively good light fastness.
Application: Pre-treated fabrics, post-process steaming, and fastness wash required.
- Acid dye on polyamide (nylon), silk, and wool for sportswear, swimwear, lingerie, and accessories including ties and scarves.
Characteristics: bright colors, good wash fastness and good light fastness.
Application: Pre-treated fabrics, post-process steaming, and fastness wash required.
-
Disperse dye (dye sublimation, and direct disperse inks) on polyester, for sportswear, fashion products, interior products, accessories, and promotional products.
Characteristics:
a. Dye sublimation inks: brilliant colors, good light fastness;
Application: no pre-treated fabrics transferred and fixed in a heat press, no wash.
b. Direct disperse inks: excellent light fastness, for outdoor applications like flags;
Application: Pre-treated fabrics, heat fixation and fastness wash required. -
Pigments using resin binders to attach on fabric surface, used across a very wide range of fabric types;
for fast fashion products, interior products, and promotional products (like cloth bags).
Characteristics: low wash fastness, very good light fastness, affecting the 'feel' from stiff to sticky, depending on the binder;
Application: Simple print application process; pre-treated fabrics preferred, after treatment preferred, dry-heat fixation required, no wash. -
Vat dye on cotton, linen, and viscose, used to print textiles for high-end furnishing and military uniforms.
Characteristics: Vat dyes have excellent wash and light fastness ratings.
Application: Pre-treated fabrics, post-process steaming, and fastness wash required.
What is reactive printing?
Printing with reactive dyes is used on cellulosic fabrics, such as cotton and viscose, (incl, EcoVero, Tencel and Lyocell) and other natural fabrics like silk. Reactive dyes require a dedicated steam fixation process to link the dye with the fibres of the fabric to preserve the color for long-lastingness. It also involves increased production costs and dedicated technology expertise, resource consumption and appropriate machinery. So not every digital fabric printing house offers reactive printing.
Using reactive dyes is still the best method of printing on cellulosic and natural fibres delivering the high-quality, long-lasting, sustainable prints which are resistant to washing, fading and cracking as desired for high-end fashion.
What is pigment printing?
Pigment printing can be used on a wide range of materials. Printing with pigments on cotton textiles is predominant, also the use of fabrics of Lyocell or usual viscose and especially for fibre mix like polyester/cotton. Pigments have no interaction with the fibres, they are not material specific. The pigment itself do not form a bond with the fabric material, but rather “stick” to almost any surface using an adhesive layer (binder).
Digital pigment printing results in a surface coloring of the fabric only. Therefore, the colorful pattern is on top of the fabric, while the underneath stays in its natural, usually white, color. Using pigments is still the best method when high light fastness is required e.g. curtains, where low rub or wash fastness is no issue.


What are the pros and cons of Reactive / Pigment printing?
The advantage of pigment printing is for sure its process simplicity. Proper pigment print application does require post processing steps like curing (fixation) and applying a finishing for a better fastness and feel.
Pigments do not seep into the fabric, as in the case of reactive dye printing. This is also linked to the longevity of such coloring, which is shorter than reactive dye printing. As a surface printing method, pigment ink prints are vulnerable to more rapid, continuous washing out and the associated constant fading. After more or less washes, the colors lose their intensity steadily. Pigment printed fabrics do not tolerate rubbing very well, especially when wet, which can manifest itself in abrasion marks after washing.
Very intense and dark colors are difficult to achieve; pigment favors pastel prints. Although black printing is possible, pigment inks will not be the best choice for printing black patterns.
Pigmented prints are easily recognizable. They generally have a stiffer character than prints with dyes like reactive dyes, which is due to the binder system of pigment printing.
Due to the lower wash fastness, part of the pigment is washed out in household laundry every time the product gets washed and ends up in the wastewater still.


1. Upper left washed Pigment print / Lower right washed Reactive print 2. Left washed Pigment print / Right washed Reactive print
Reactive printing produces vibrant, deep colors that are long-lasting. The reactive dyes penetrate the fabric and create a permanent bond with the fibres during fixation, producing colors that do not fade or peel over time or repeated washing.
The reactive dye, dedicated fabric pre-treatment in a steam fixation process cause a chemical reaction that forms a covalent firmly bond of dye and fibre. The reactive dyes have no influence of the natural hand feel of a fabric. After dye fixation the printed fabric undergoes a fastness wash to remove the small part of unreacted dye (no chemical reaction occurs 100%) and pre-treatment, resulting in a vibrant, long-lasting print.
The long-standing criticism of reactive printing is its water consumption. Due to its application process requiring wash-off of unreacted dyes and pre-treatment, in (low-wage) countries with fewer regulations, this can lead to untreated wastewater flowing into surrounding rivers and harming the environment.
We at House of U use highly advanced washing machines specialized in high-efficient washing using the amount of water necessary only. We also dispose our waste water responsibly and have our process evaluated to ensure it’s eco-friendly and free of harm.
For which products reactive printing can be used?
Reactive printing can be used on a variety of fabric products like custom printed unique designs for apparel/fashion products, to create custom designs for interior products, such as curtains, tablecloths, and pillowcases as well as for accessories such as bags.
What lasts longer, pigment or reactive printing?
Both pigment printing and reactive printing have their strengths and weaknesses. Pigment printing is a versatile method for printing on a variety of surfaces, while reactive printing is best suited for cellulose-based materials and producing high-quality, vibrant, durable prints. The choice between the two methods ultimately depends on the specific needs of the project and the desired quality standards.
What is cheaper?
Pigments need to be fixed but do not need to be washed. Pigment inks are more expensive and less color intense than reactive inks. They often require 2-3 times as much ink for the same color, which also affects the printing speed.
Screen printing vs digital printing
Conventional screen printing and digital (inkjet) printing are two different methods for applying the color onto fabrics. While both methods can produce high-quality prints, there are significant differences between the two like, freedom of design, the printing process, and the print result.
Screen Printing
Screen printing, also known as silk screen printing, is a conventional printing technique that involves transferring printing paste onto the fabric via a mesh screen. The mesh screen is stretched over a frame, and by blocking out areas that are not meant to be printed the desired motif is printed on the fabric. For each color of the print motif a separate screen template must be produced.
When printing, color paste is then applied to the screen and pressed through the open areas of the screen with a squeegee. This process is repeated with the different screens (one for each color) of a design until all the desired colors of the motif are printed. Also, the printing process is repeated for the needed fabric length.
Screen printing is a cost-effective method for printing large quantities of a design. However, screen printing is not suitable for short runs and for printing very fine details or delicate designs and soft color gradients, as the size of the mesh openings in the screen play a role as a type of grid dots. Also, it gets more costly for more colors in an image.
When screen printing, the contents of the machine system (squeegee, screens, and supply pipes) are always residual paste after printing. This residue must be washed off and drained, thus producing wastewater.
Digital Printing
With Digital printing, also known as Inkjet Printing, the digital image / color data of a design is directly available for contactless printing without the need of producing screens and fixed repeats based on screen dimensions to cover the fabric in the width and length for a seamless print. Digital printing also allows the possibility of printing a quantity of one and makes an on-demand business model possible.
Therefore, with the upcoming digital printing techniques we saw a business model shift: enormous amounts of (unsold) inventories are outdated. To address sustainability goals business must shift to a truly on-demand mode, produce sold items only, improved lead times and much lower return rates. Digital printing can thereby reduce the amount of carbon emissions, water, wastewater, and electricity. Not to forget raw materials as you don't have any screens left over that you have to store away, in many cases until eternity, Digital printing has truly environmental benefits.
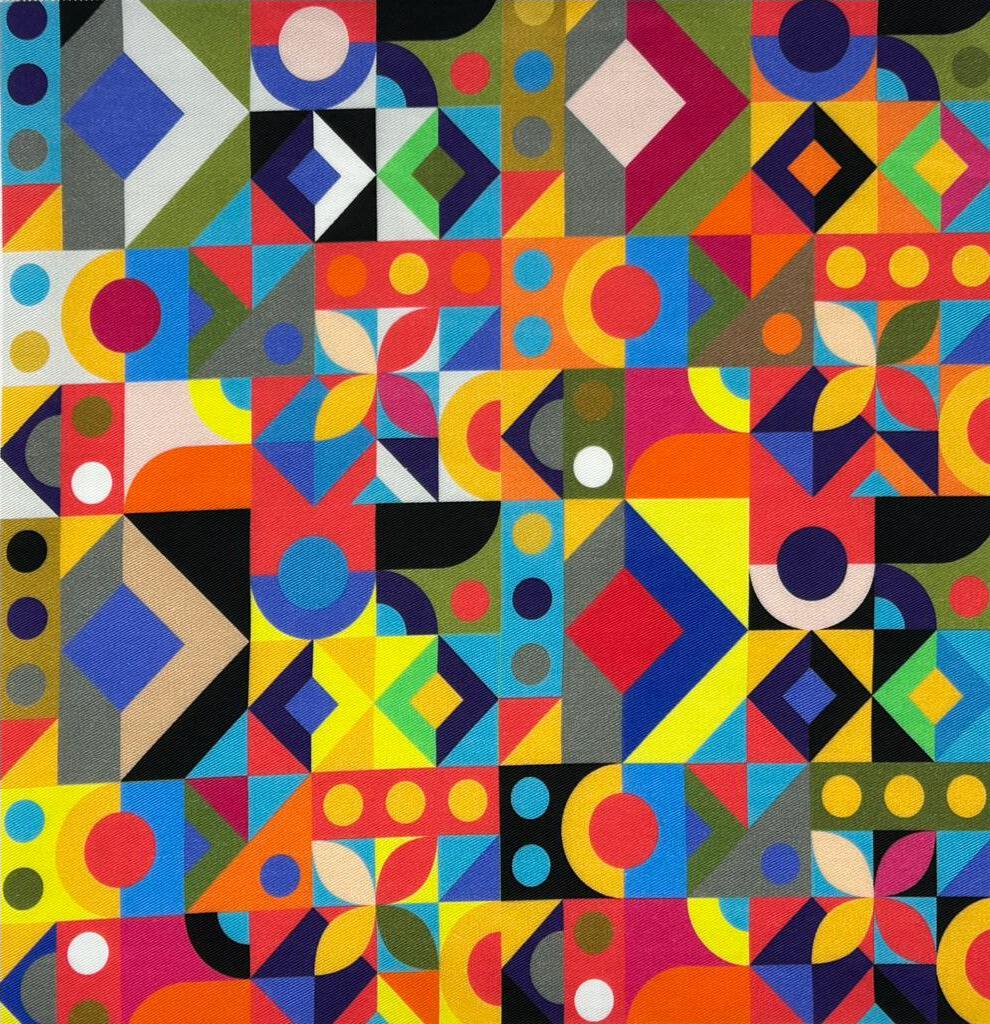
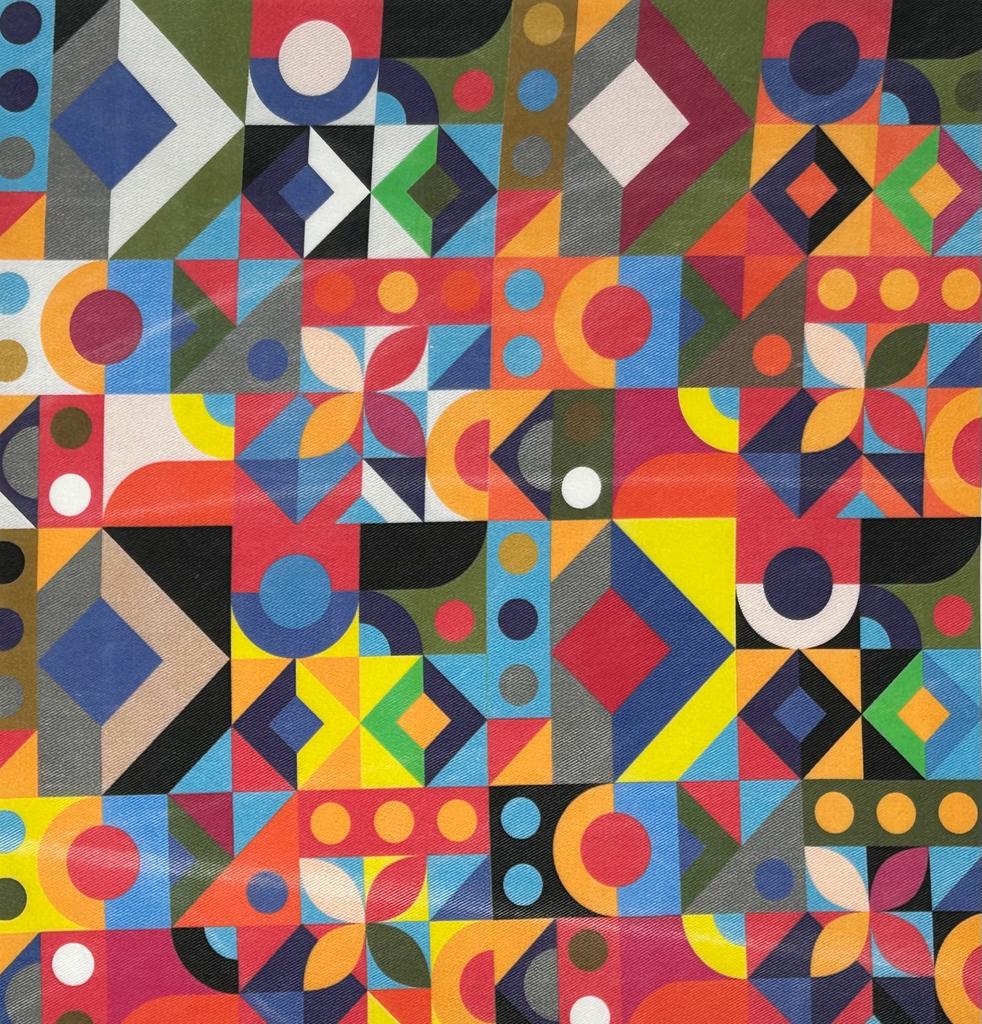


1. Reactive after washing / 2. Pigment after washing
Why we use the inkjet printing technique with reactive dyes at House of U?
At House of U we have chosen to offer digital reactive printing services intentionally because it the best method of printing on cellulosic and natural fibres still, delivering the highest quality level of color vibrant as well as durable, thus sustainable, printed fabrics even after repeated use and after several washes.
We follow technology developments constantly. This technology can help, to produce better. Sustainability and print-on-demand will be the key points for the future.
Custom printed fabrics at House of U
Do you want your own design printed on fabric by the yard. This is very easy at House of U. You can upload your design in our design tool and have this printed on a fabric of your choice from our collection.
Do you still find it difficult to choose and would you rather see and feel our fabrics first? Then order the fabric swatches you want. Or you can order our complete fabric book or the Eco Fabric Kit, which contains all our sustainable fabrics.
If you’re want some more advice, feel free to contact us. We’re always happy to help!









